Session Description: Harness the power of AI to help you better support English Learners (ELs) in your ELA classroom. Explore cutting-edge AI tools that offer personalized learning experiences, catering to the diverse linguistic needs of ELs. From adaptive language exercises to real-time translation aids, discover how AI can dismantle barriers, foster inclusivity, and provide a scaffolded approach to mastering the nuances of language arts.
Getting Started

I am super excited to be presenting again for BER. Welcome to your outsourced memory for today’s session. Not sure what outsourced memory is? No worries, you simply haven’t learned about outsourced memory and transactive thinking YET! But we will get to that shortly. Please feel free to follow along here as we go through this session. Please feel free to share this resource with others, and if you have questions, or would like to share something with me, feel free to email me.
AI Video above made with Veed.io. Yes, you can create your own avatars and have them say whatever you want. So, what virtual teaching assistants might you create?
7 Things + or – 2 that everyone should know about AI

In this next section we are going to address the elephant in the room, we are going to discuss a variety of topics related to AI and language teaching so that you can become aware of things you may not know. If you have questions, ask them. If you have concerns, voice them. We often don’t know what we don’t know, so let’s start with the least you should know about AI detection.
So what is a GPT?
- Generative: This means it can create content like text, images, or video based on the patterns and information it has learned. It essentially has the ability to generate content.
- Pre-trained: Before you even start using it, the model has already been trained on a huge dataset of text from books, websites, and other sources to understand a wide variety of languages.
- Transformer: This is the type of model architecture used. It’s particularly good at understanding the context of language, meaning it can understand how words in a sentence relate to each other.
What are LLMs? Why Should I Care?
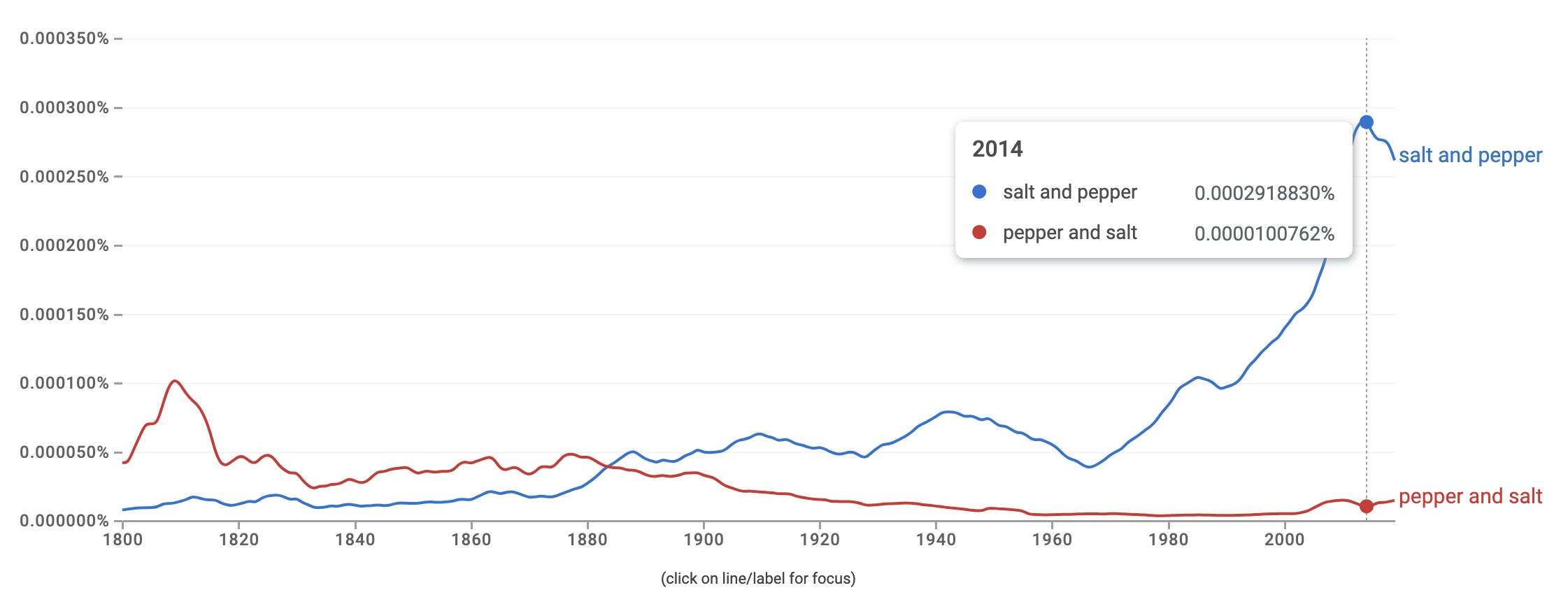
Google’s Ngram Viewer is an online search tool that allows users to explore the frequency of specific words or phrases (ngrams) in a vast corpus of books and other texts over a specified period. This corpus includes millions of books digitized as part of Google Books, covering a wide range of languages and spanning several centuries. Additional Search Options
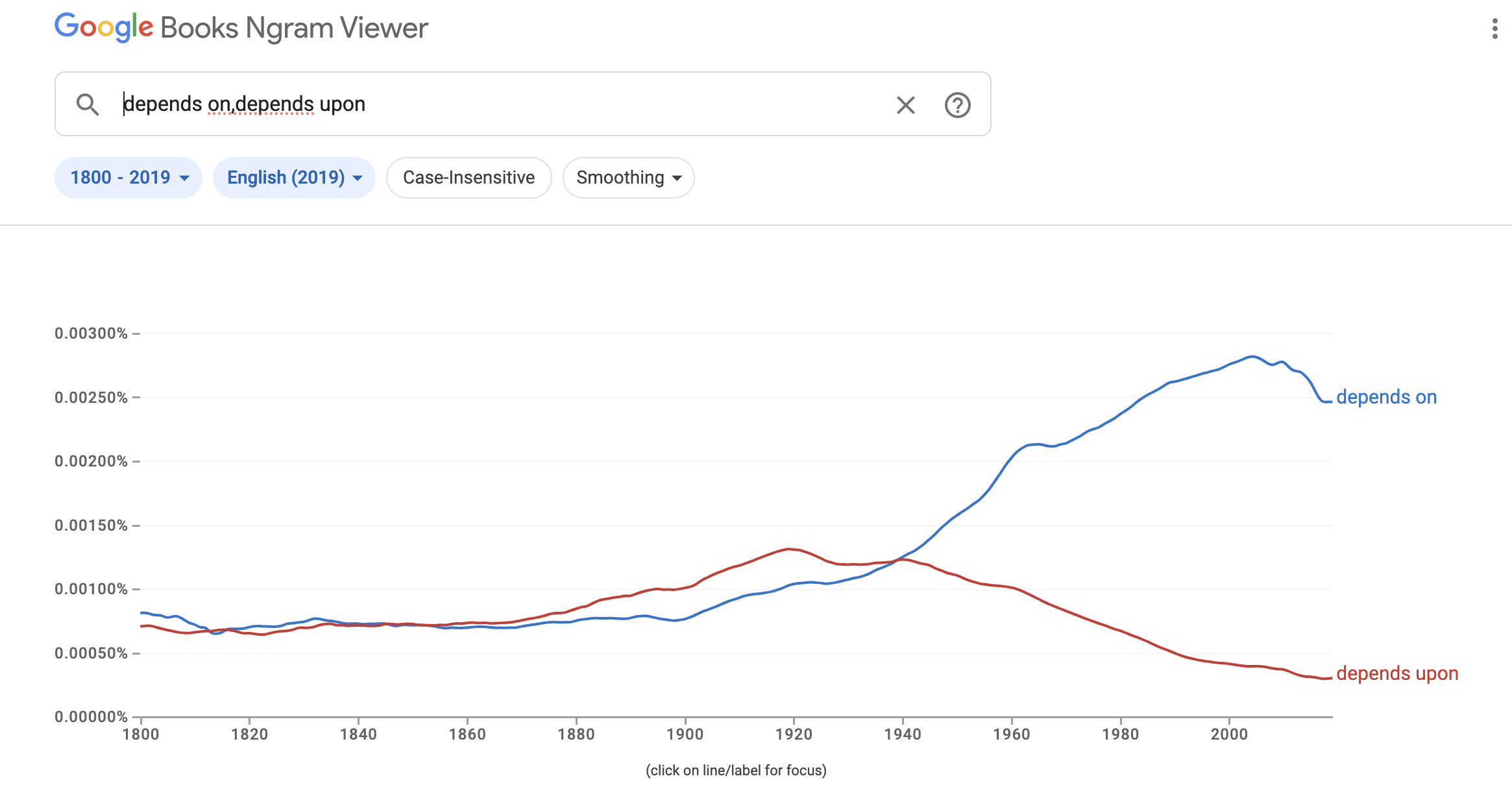
AI uses corpus based data and context to predict which words it should use
- Frequency Analysis: During training, the model analyzes how often words and phrases appear in context with each other. This frequency information helps the model learn the likelihood of a specific word following another in a sentence.
- Probabilistic Predictions: Based on this frequency analysis, the model builds a probabilistic understanding of language. For instance, in the phrase “peanut butter and,” the word “jelly” might appear more frequently than “cheese” in the training data, so the model will learn that “jelly” is a more likely prediction.
- Contextual Relevance: Beyond mere frequency, modern AI models like transformers also consider the broader context of words in a sentence or paragraph, which enhances their ability to make relevant and coherent predictions. This means that the model doesn’t just rely on the immediate previous word but evaluates the entire context to make a more informed prediction.
The importance of context when prompting AI
What do you mean by AI is language agnostic?
Here is a link to an updated version of my agent.
Some AI teaching Ideas
- Using AI to Differentiate Learning
- Using AI to develop scenario based learning
- Using AI to develop scripts
- Using AI to develop “lesson specific” chatbots to get interactive feedback
- Using AI to create annotation assignments for active reading.
- Chapter summaries or “The Least You Should Know”
- Using AI to develop pre-mails and outreach emails
- Creating bottomless quiz and survey pools (Retrieval Practice/Enhanced Test Security)
- Using AI to develop enhanced prompts & instructions (Retrieval Practice/Content building)
- Using AI to develop enhanced discussion topics and threads (Course Analysis, review, re-design)
- Using AI to develop/enhance rubrics in Canvas (student feedback)
- Analyze quiz questions and develop explanations and follow up instruction responses (Enhanced Student Feedback)
- Creating AI Chatbots or AI Prompts to help students analyze and get additional feedback from written assignments (Personalized Feedback)
- Have AI design Text Expanded Feedback in Canvas (Practical Applications for Fast Feedback)
Picking a Team, Which AI Should I Learn?
- ChatGPT – ChatGPT is a chatbot and virtual assistant developed by OpenAI and launched on November 30, 2022. Based on large language models, it enables users to refine and steer a conversation towards a desired length, format, style, level of detail, and language
- Claude – Claude is a family of large language models developed by Anthropic. The first model was released in March 2023. Claude 3, released in March 2024, can also analyze images.
- Gemini – Google Gemini is a family of multimodal large language models developed by Google DeepMind, serving as the successor to LaMDA and PaLM 2, positioned as a competitor to OpenAI’s GPT-4.
- Copilot – Microsoft Copilot is a generative artificial intelligence chatbot developed by Microsoft. Based on a large language model, it was launched in February 2023 as Microsoft’s primary replacement for the discontinued Cortana.
- Llama – Llama (acronym for Large Language Model Meta AI, and formerly stylized as LLaMA) is a family of autoregressive large language models (LLMs) released by Meta AI starting in February 2023. The latest version is Llama 3, released in April 2024.

When is the best time to plant a tree?
Pick a topic. Any topic!
Prompting 101 – Saying NO to GIGO!
AI Prompts for Teaching: A Spellbook
This guide demonstrates how carefully crafted prompts allow you to harness AI as a teaching and learning partner. You’ll find prompts to enhance course design, improve your own skills, provide student support, adapt content, and boost relevance and comprehension. With thoughtful prompt engineering, AI can save you time while also improving pedagogy and student outcomes.
The CRAFT Method
As educators, particularly for English Language Learners (ELLs), integrating Artificial Intelligence (AI) into the learning environment can be transformative. The key lies in the art of crafting prompts that are not only effective but also strategic in their design. The CRAFT mnemonic is an excellent guide to achieving this:
- Call to Action Begin by explaining what you would like to do and use action verbs so the AI knows what you are hoping your students will be doing. This could be “describe,” “compare,” “argue,” or “create.” Your prompt should guide AI to generate responses that prompt students to apply their knowledge actively and engage in language practice.
- Role: Define the role for your AI, let it know that you need it to act as an expert in ELL, instructional design, pedagogy, ideation, lesson planning, etc.
- Audience: Explain to the AI who your audience is. I teach 6th grade English Language Learners with lexile levels from 650 to 850. They are very interested in …
- Format: Specify the format of the response expected. Will the AI generate a dialogue, a letter, or a report? This allows you to create content for students to practice different writing styles and structures, which is crucial for their language development.
- Technical Requirements: Outline any specific requirements that the response should meet. This includes grammar focus, vocabulary usage, word count, or any particular content that needs to be included. This could also include output requirements like html. This helps ensure that the AI’s response aligns with the educational objectives.
The 20 Questions Method
Engaging in a “20 Questions” dialogue with AI involves having the AI ask a series of questions about your goals, teaching style, and specific needs. By answering these questions in detail, you provide the AI with rich context, enabling it to generate more relevant and personalized suggestions. This method enhances the AI’s effectiveness in ideation and content creation, ensuring that its responses align closely with your objectives and writing style.
Are you BG? or AG?
Google – Google Images – Google Scholar – Google Drive – Google News – Youtube
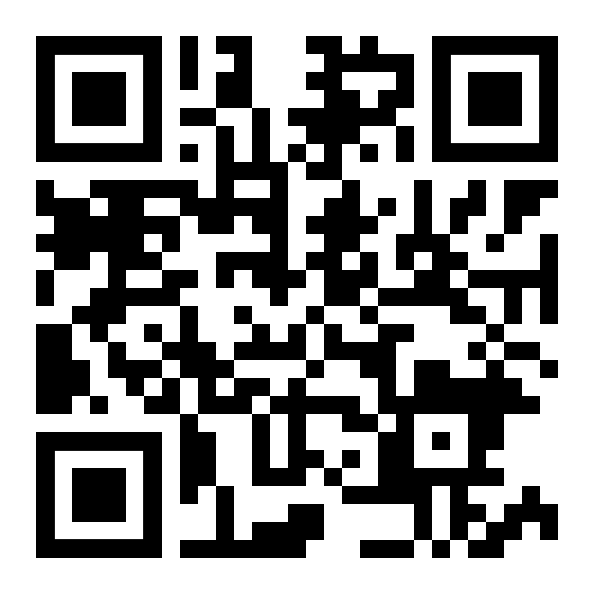

You likely have a built in QR Code scanner in your smart device. Just turn on your camera app and point it at a QR code. Want to learn how I created the QR codes for today? Click here QRCode Monkey is a 100% free QR code generator. It is also a great tool for differentiating content in your classroom. Need to be in more than one place at one time? QR code can be your buddy.
Google Proof Your Content with Blooms Taxonomy
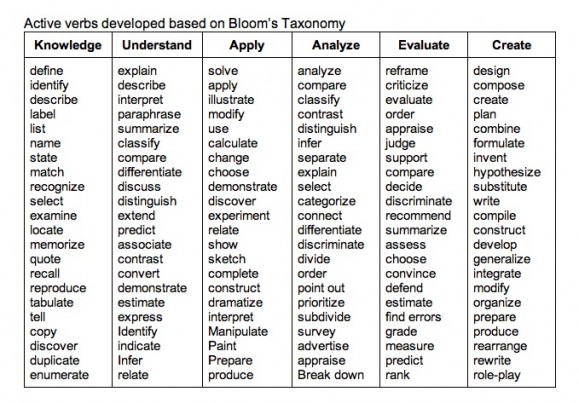
Question: What are the parts of a cell?
Google Proof Question: Rank the importance of the parts of the cell from least to most important.
What about AI Detection?
A Word or Two about F.E.R.P.A
What is FERPA?
The Family Educational Rights and Privacy Act (FERPA) is a federal law that protects the privacy of student education records. It applies to all schools that receive funds from the U.S. Department of Education. FERPA grants specific rights to parents and students regarding access to education records, the right to seek amendment of those records, and control over the disclosure of personally identifiable information (PII).
- Consent Requirements: Before using any AI tool that requires student data, check if parental or student consent is needed. For any technology that may involve external parties handling student data, written consent to share data is generally required unless the information has been de-identified.
- Legitimate Educational Interest: If you are using AI tools within the school environment, such as learning management systems that integrate AI for personalizing learning, ensure that these uses fall within the scope of “legitimate educational interests.” This typically includes activities that are directly related to the academic and administrative functions of the school.
- De-identification of Data: If AI tools require data but not specifically identifiable information, consider using de-identified data to maintain compliance with FERPA. This process involves removing any personal identifiers, ensuring the data cannot be used to trace back to any individual student.
- Data Security: Ensure that any AI application used in the classroom adheres to strict data security standards to prevent unauthorized access to student information. This includes reviewing and understanding the security measures the AI provider has in place.
- Vendor Compliance: When using third-party AI tools, ensure that the vendor is compliant with FERPA regulations. This typically involves having a formal agreement that the vendor will protect the student data and will not use it for unauthorized purposes.
Power Pedagogies for Engaging Learners in an AI world

The YET Bet
Are you good at math? Do you speak another language? Why or why not? All students should learn the power of a growth mindset. As I have mentioned, am about to share some teaching technologies with you. Some of you may not see yourselves as “Technology People,” of course, I would argue, not YET! How good are you at drawing? Can you draw cartoon characters? If I could prove to you that you can draw in the next 5 minutes, would you be open to trying some of the other ideas we have to share with you today?
If you would like to learn more about making your ideas visual, check out Graham Shaw’s The Art of Communication or Dan Roam’s The Back of the Napkin. Of course, don’t forget, now there are AI’s that can do the drawing for us.
Thin-Slicing
Let’s pretend that students below are students in your class. Take a look at the images below. Can you identify what the kids are thinking or feeling? Turn to the person next to you and let them know what you think each represents. Did you both agree? Share your answers with me via this backchannel. Then discussion your answers with those sitting near you.
Do you Bitmoji?

So what is Backchanneling, and why should I care?
Challenge Question: How might you use Google Slides in your Classroom?
Additional Backchanneling Tools & Resources
Kahoot.it (Participant link) Kahoot (Presenter Link)
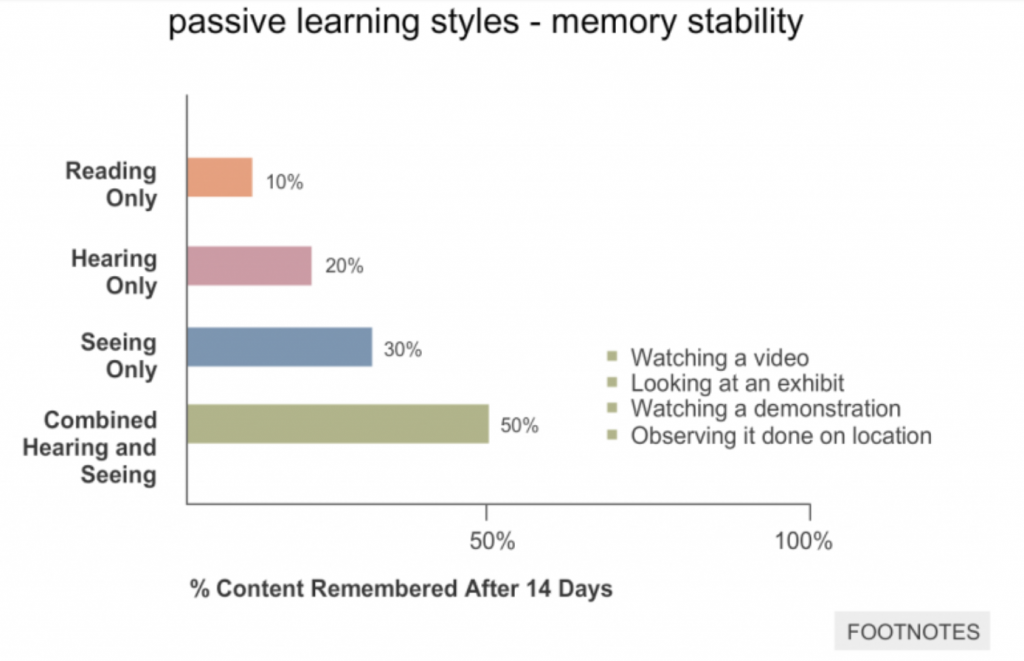
What is Retrieval Practice?
Featured in in the book Make It Stick and supported by quite a bit of research….
7ddfffe4b8896cc59be4ff0000359472/medical-education/activelearning/make-it-stick_(1).jpg?sfvrsn=3a569353_0)
Retrieval practice is a learning strategy where we focus on getting information out. Through the act of retrieval, or calling information to mind, our memory for that information is strengthened and forgetting is less likely to occur. Retrieval practice is a powerful tool for improving learning without more technology, money, or class time (RetrievalPractice.org).
What is JiTT?
Just-in-Time Teaching (JiTT) is a strategy that promotes the use of class time for more active learning. Originally developed by Gregor Novak and colleagues, JiTT relies on a feedback loop between online learning materials and the classroom (Novak et al., 1999). Teachers use online assessment tools to ask students to perform Warm-ups, Puzzles, and Goodfors The students answers to the assignments are delivered to the instructor a few hours before class starts. The teacher looks over student responses to see where students are and adapts the lesson accordingly. Teachers can also now use the responses as scaffolding on which to build learning.
Challenge Question: How might you use Google Forms to allow for retrieval practice or know how they are doing Just In Time?
The Power of Images and Video

Infographics + Canva
A little touch up? Free Fun with Pixlr
What about AI?
According the Verge, “Google has apologized for what it describes as “inaccuracies in some historical image generation depictions” with its Gemini AI tool, saying its attempts at creating a “wide range” of results missed the mark. The statement follows criticism that it depicted specific white figures (like the US Founding Fathers) as people of color, possibly as an overcorrection to long-standing racial bias problems in AI.”


Best Practices for Youtube with ELLs
Karaoke + AI Lyric Writing
TEDed + Glasp
Massive Multiplayer Thumb Wrestling & Stepping Up Your Gamification

Directing Your Own Videos – Finding Your Hidden Skills
Making Your Own Videos
Have you considered Screencasting? Screencasting is a Teacher Trick that should be in every teacher’s toolkit. Simply put, screencasting is recording your computer screen while recording your voice to make a video that can be shared with others. You can make instructional videos, feedback videos, showcase videos, interactive videos and more. While there are many tools that teachers can buy for screencasting, there are now some really great ones that are free and play right in the browser. Below, I have put a few options for you. Which tool you pick really depends on what your plans are for using the tool. Are you using it yourself to make and host videos? Did you want students to use the tool?
Flip is now part of Microsoft Teams for Education
Are there any other AI’s I should know about?
Twee Create content for your classroom
Ideogram is a free-to-use AI tool that generates realistic images, posters, logos and more.
Canva Magic Studio All the power of Canva’s AI, all in one place. Magic Studio™ brings together the best AI-powered tools for you and your team, right inside Canva.
Diffit Differentiate your teaching
Goblin.tools A Magic ToDo list creator and more
MagicSchool 60+ of the incredible AI tools for educators in MagicSchool
Conker AI powered Assessments
Firefly Free Text to image AI from Adobe
Glasp Youtube Summarizer Pluggin that will connect Youtube to ChatGPT or Claude
D-ID Image to video AI
Snorkl students record and share their reasoning then receive
instant AI-powered feedback to drive deep and meaningful learning.
Sherpa Voice-enabled assignments for students to chat about class material
Descript Voice Cloning and Much More
Khanmigo Khan Academy’s AI Pilot
📋 Expand for Video Highlights:
- 00:00Links to an external site. AI can revolutionize education by providing every student with a personal tutor and every teacher with a teaching assistant.
- 01:59Links to an external site. Khan Academy’s AI tutor, Khanmigo, can detect and correct student mistakes, identify misconceptions, and prompt students to explain their reasoning.
- 03:19Links to an external site. Understanding context is crucial in computer programming exercises, even for non-computing backgrounds, and a platform can help with video comprehension, quizzes, and idea connections.
- 05:01Links to an external site. Khanmigo offers comprehensive coaching services for students, as shown by the launch of GPT-4 and the success of Khan World School.
- 07:10Links to an external site. Students can debate with AI on canceling student debt and use AI writing tools to collaborate on writing, while Khanmigo’s prototype uses generative AI to enhance reading comprehension.
- 09:30Links to an external site. AI technology and Khan Academy’s teacher mode help improve student writing skills and save time for teachers.
- 11:23Links to an external site. AI-powered education can be revolutionized with large language models like GPT-4, which can improve math and tutoring by allowing AI to think before speaking.
- 13:37Links to an external site. AI debate split between pessimistic and optimistic views, but active participation needed to ensure positive use cases and prevent dystopian future.
Other tools to consider with ELLs
Geogebra – Solve equations, graph functions, create constructions, analyze data, explore 3D math! y=2x+3
xtramath – A free web program to help students learn Math
Read Theory – A free adaptive learning program to help students practice their reading skills.
Quill – provides free writing and grammar activities for middle and high school students.
Unite for Literacy – provides free digital access to picture books, narrated in many languages.
Storybird – lets anyone make visual stories in seconds.
Apptivities

Words from letters – A quick game for practicing word knowledge, spelling, and transactive thinking
Wordhippo page 21 – A dictionary that also finds synonyms, antonyms, words that rhyme with it, sentences containing it, other words starting or ending with it, its etymology, and much more.
Trivia Challenge – Give your students authentic reasons to practice their Google Skills
Fact or Fiction Challenges
- The Great Emu War: In 1932, Australia faced an unexpected foe – emus. The birds were causing chaos in Western Australia, leading to a military operation against them. Despite the use of machine guns, the emus proved surprisingly resilient, and the birds emerged victorious.
- The Dancing Plague of 1518: In Strasbourg, France, a woman began dancing in the street, and within a month, hundreds of people had joined her, dancing for days without rest, leading to numerous deaths. The cause of this dancing mania remains a mystery.
- Tarrare, the Insatiable Eater: In 18th century France, a man named Tarrare had an appetite so voracious he could eat a quarter of a cow in a day. His inexplicable condition led him to consume everything from stones to live animals, and even, allegedly, a human heart.
- The Rain of Fish in Honduras: In the city of Yoro, an unusual meteorological phenomenon occurs annually known as “Lluvia de Peces” (Rain of Fish), where fish are found on the ground after heavy rainstorms. Scientists believe tornadoes or waterspouts may pick up the fish from rivers and drop them over the land.
- The Green Children of Woolpit: In the 12th century, two children with green-tinged skin mysteriously appeared in the village of Woolpit in England. Speaking an unknown language and refusing all food except beans, their origin remains a subject of speculation and wonder.
- The Toxic Lady: In 1994, Gloria Ramirez was admitted to a California hospital with severe health issues. Hospital staff treating her began fainting and experiencing symptoms of poisoning when exposed to her blood and body. The cause remains a controversial mystery, with some suggesting toxic fumes were released from her body.
- The Phantom Barber of Pascagoula: In 1942, a mysterious figure known as the Phantom Barber would break into homes at night in Mississippi, not to steal, but to cut the hair of sleeping occupants. The bizarre motive behind these break-ins was never fully understood.
- Cleopatra’s Needle and the Curse of the Pharaohs: When the ancient Egyptian obelisk known as Cleopatra’s Needle was transported to London in the 19th century, it was rumored to bring a curse with it. Stories of bad luck and bizarre incidents followed, part of the larger myth of the curse of the pharaohs that affects those who disturb ancient Egyptian tombs.
- The Zone of Silence: Located in Mexico, this desert patch is known for its peculiar properties, including non-functioning radios and compasses, and is often compared to the Bermuda Triangle. It’s said that meteorites frequently fall in the area, leading to speculation about magnetic anomalies.
Readers Theatre – Use readers theatre in the classroom or have students record or get creative with animation.
Color Alive – Have students color a character and write about it, then bring that character to life in front of their eyes with Augmented Reality.
Faceswap Live – Trade faces with students or where someone else’s face to make a presentation. Don’t give a presentation of Abraham Lincoln, give one as Abraham Lincoln.
Will We Become Coopers?
There are numerous family names that have fascinating origins tied to people’s historic occupations and professions. For instance, surnames like Fisher, Miller, Carpenter, Baker, Taylor, and Cooper, to name a few, offer intriguing glimpses into the lives and trades of our ancestors. Let’s delve into the world of Coopers for a moment. Coopers were skilled craftsmen who displayed mastery in crafting and repairing wooden buckets, barrels, and casks, essential containers for storing and transporting various goods. However, if you look around today, you’re unlikely to encounter many individuals bearing the name Cooper who still practice the trade.

Clarke’s first law
When a distinguished but elderly scientist states that something is possible, he is almost certainly right. When he states that something is impossible, he is very probably wrong.
Clarke’s second law
The only way of discovering the limits of the possible is to venture a little way past them into the impossible.
Clarke’s third law
Any sufficiently advanced technology is indistinguishable from magic.